Cerebral Edema Treatment Guidelines
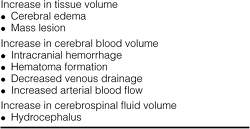
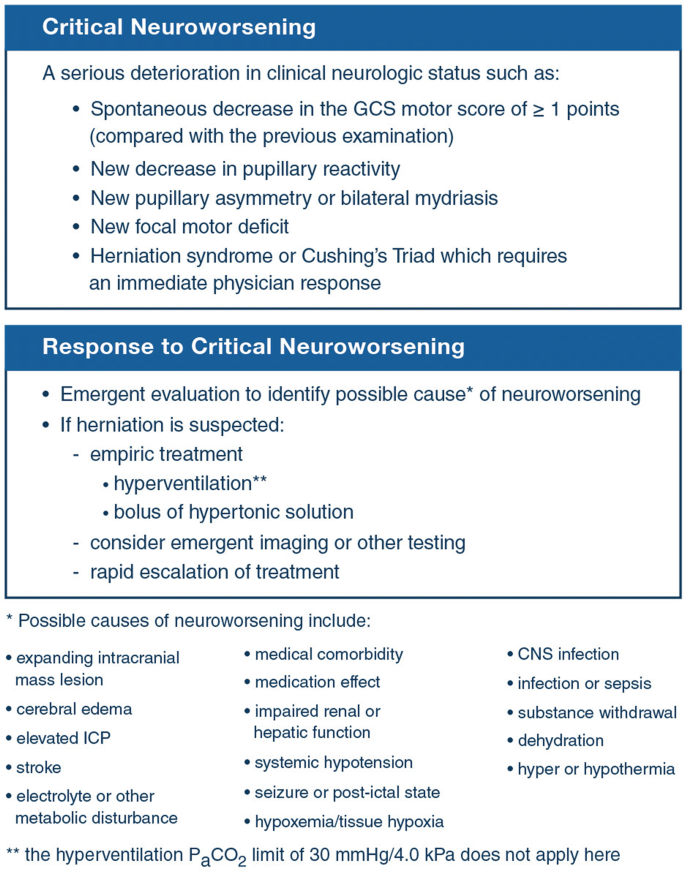
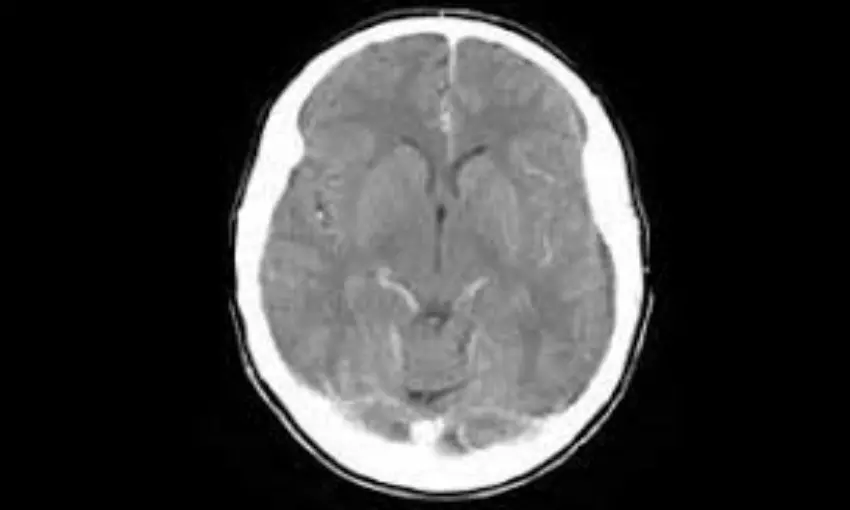
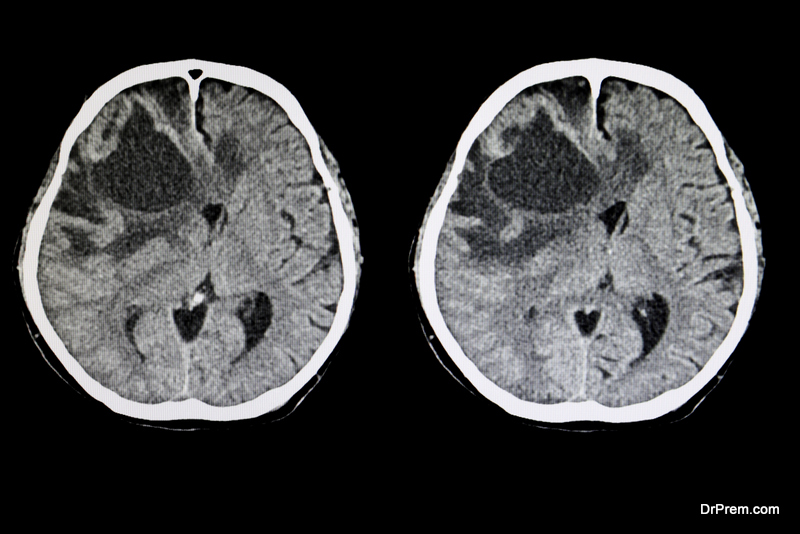
Cerebral edema treatment guidelines. Cerebral Edema in Neurocritical Care Patients Clinical Practice Guidelines NCS 2020 2020 guidelines for the acute treatment of cerebral edema in neurocritical care patients Guidelines. Clinicians must be able to select appropriate therapies for initial cerebral edema management based on available evidence while balancing efficacy and safety. The development of clinically significant cerebral edema is expected only in large-territory cerebral infarcts and can be observed by the clinician in 3 ways.
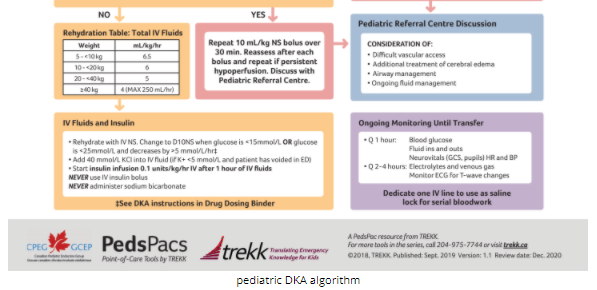
Children presenting with more severe DKA higher blood urea nitrogen levels and more severe acidosis and hypocapnia are at greatest risk 1-4. This guideline evaluates the role of hyperosmolar agents mannitol HTS corticosteroids and selected non-pharmacologic therapies in the acute treatment of cerebral edema. Sedation to lower cerebral metabolism and hyperosmotic agents to directly reduce cerebral edema are the cornerstones of therapy.
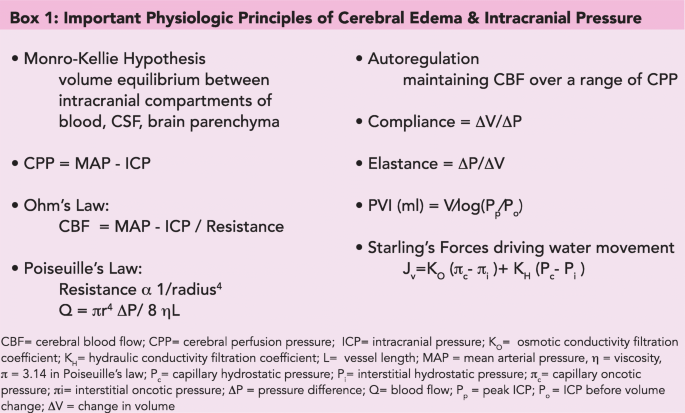
While our understanding of cerebral edema and its pathogenesis have expanded dramatically in the last decade treatment options are still limited. Clinicians must be able to select appropriate therapies for initial cerebral edema management based on available evidence while balancing efficacy and safety. This complication is far more common among children with DKA than among adults.
Hawryluk3Patrick Mailloux 4Diane McLaughlin 5 Alexander Papangelou6Sophie Samuel 7Sheri Tokumaru 8Chitra Venkatasubramanian 9Christopher Zacko 10 Lara L. Hypertonic saline solutions HTS are recommended in the settings of subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhage due to the potential risk of hematoma expansion when using mannitol. Drugs to reduce swelling and prevent blood clots constitute the first step of treatment.
Patients with glioblastoma commonly develop vasogenic edema. Osmotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for cerebral edema. In patients with swollen supratentorial hemispheric ischemic stroke routine intracranial pressure monitoring or cerebrospinal fluid diversion is not indicated but in patients who continue to.
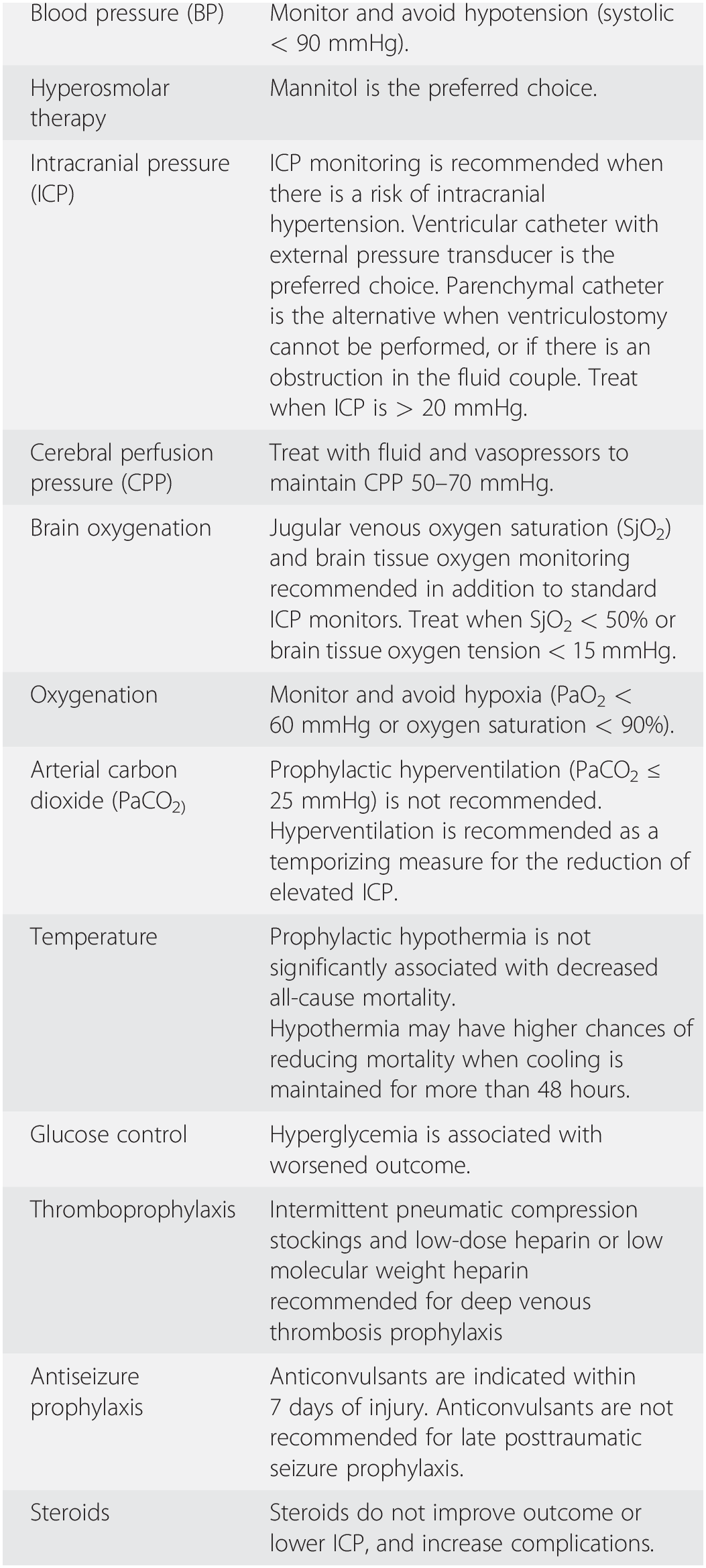
The available evidence suggests hyperosmolar therapy may be helpful in reducing ICP elevations or cerebral edema in patients with SAH TBI AIS ICH and HE although neurological outcomes do not appear to be affected. Morgan Jones 2Gregory W. HTS are recommended over mannitol in the setting of traumatic brain injury and ischemic stroke with mannitol.
Medical Treatment of Cerebral Edema. Assign code 3485 Cerebral edema as an additional diagnosis since the provider has evaluated and documented the clinical significance of the vasogenic edema.
Children presenting with more severe DKA higher blood urea nitrogen levels and more severe acidosis and hypocapnia are at greatest risk 1-4.
Guidelines on the acute treatment of cerebral edema. Cerebral injury cerebral edema is an uncommon but potentially devastating consequence of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. Medical Treatment of Cerebral Edema. HTS are recommended over mannitol in the setting of traumatic brain injury and ischemic stroke with mannitol. Assign code 3485 Cerebral edema as an additional diagnosis since the provider has evaluated and documented the clinical significance of the vasogenic edema. This guideline evaluates the role of hyperosmolar agents mannitol HTS corticosteroids and selected non-pharmacologic therapies in the acute treatment of cerebral edema. Surgery may be advised in severe cases of cerebral edema. Ventriculostomy to relieve obstructive hydrocephalus after a cerebellar infarct should be accompanied by decompressive suboccipital craniectomy to avoid deterioration from upward cerebellar displacement. Hawryluk3Patrick Mailloux 4Diane McLaughlin 5 Alexander Papangelou6Sophie Samuel 7Sheri Tokumaru 8Chitra Venkatasubramanian 9Christopher Zacko 10 Lara L.
This may have one. HTS are recommended over mannitol in the setting of traumatic brain injury and ischemic stroke with mannitol. 2 5 Currently no methods are available to predict the course. This complication is far more common among children with DKA than among adults. Osmotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for cerebral edema. Children presenting with more severe DKA higher blood urea nitrogen levels and more severe acidosis and hypocapnia are at greatest risk 1-4. Assign code 3485 Cerebral edema as an additional diagnosis since the provider has evaluated and documented the clinical significance of the vasogenic edema.



























Post a Comment for "Cerebral Edema Treatment Guidelines"