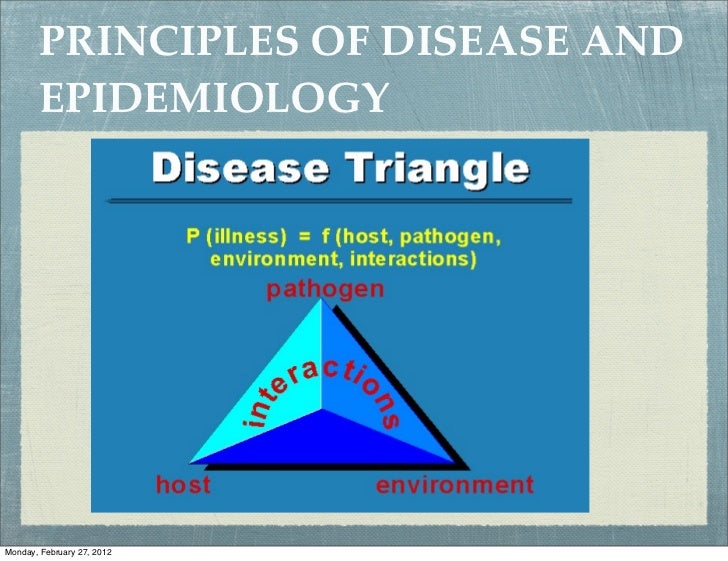
Principles Of Disease And Epidemiology
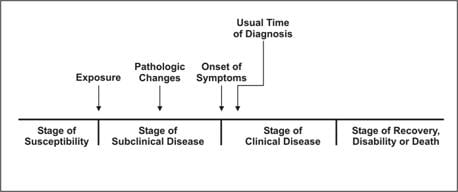
Principles of disease and epidemiology. Natural history of a disease is the evolution of disease over time from the earliest stagepre-pathogenesis to the disease stagepathogenesis to recovery disability of deathlate pathogenesis stage Its unique for each disease even different individuals Pre-pathogenesis- disease process favours the agent- it reflects the. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Many epidemiologic concepts were originally developed in studies of infectious diseases.
Describes basic epidemiology principles concepts and procedures Provides a solid foundation for the study and teaching of applied epidemiology Explains how to calculate and interpret frequency measures rations proportions and rates and measures of. Occurs when an infection results in a change from a state of health. Epidemiology is a health care discipline with an important distinction.
Fraction of a population having a specific disease. Department of Health and Human Services1992. Epidemic refers to an increase often sudden in the number of cases of a disease above what is normally expected in that population in that area.
Epidemiology is concerned with the distribution and determinants of health and disease morbidity injury disability and mortality in populations. Book provides an introduction to the basic principles and methods of epidemiology. Specifically epidemiology uses science systems-thinking and data to determine the underlying causes of different diseases and health outcomes in a population.
Key terms in this definition reflect some of the important principles of epidemiolog y. The purpose is to describe and identify opportunities for intervention. Disease that is EASILY spread from one host to another.
Occasionally the amount of disease in a community rises above the expected level. Xexplain the principles of. Invasion or colonization of the body by pathogenic organisms.
Epidemiology is the study of health- related trends in population for the purpose of disease prevention. Epidemiology Study occurrence of disease and disease transmission in populations Etiology disease patterns contributing factors Results used in public health to develop methods of disease prevention Also measure effectiveness of public health program Assesses effectiveness of clinical procedures.
Epidemiology is a health care discipline with an important distinction.
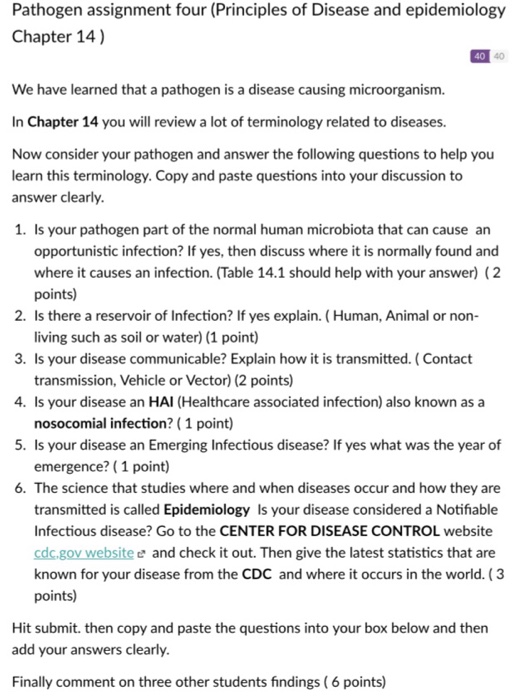
Epidemiology is the study of transmission incidence and frequency of disease in order to identify cause source and route of transmission. Epidemiology is a health care discipline with an important distinction. The purpose of this book is to. Key terms in this definition reflect some of the important principles of epidemiolog y. Xexplain the principles of. Studies how disease develops. Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and determinants factors of health-related states or events in specified populations and the application of this study to the control of health problems. Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Introduction u Pathologyis the scientific study of disease. Occurs when an infection results in a change from a state of health.
Book provides an introduction to the basic principles and methods of epidemiology. The object of screening for disease is to discover those among the appar ently well who are in fact suffering from disease. Many epidemiologic concepts were originally developed in studies of infectious diseases. Disease that is EASILY spread from one host to another. Epidemiology is a health care discipline with an important distinction. Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Introduction u Pathologyis the scientific study of disease. Invasion or colonization of the body by pathogenic organisms.







































Post a Comment for "Principles Of Disease And Epidemiology"