Interferon Treatment For Melanoma
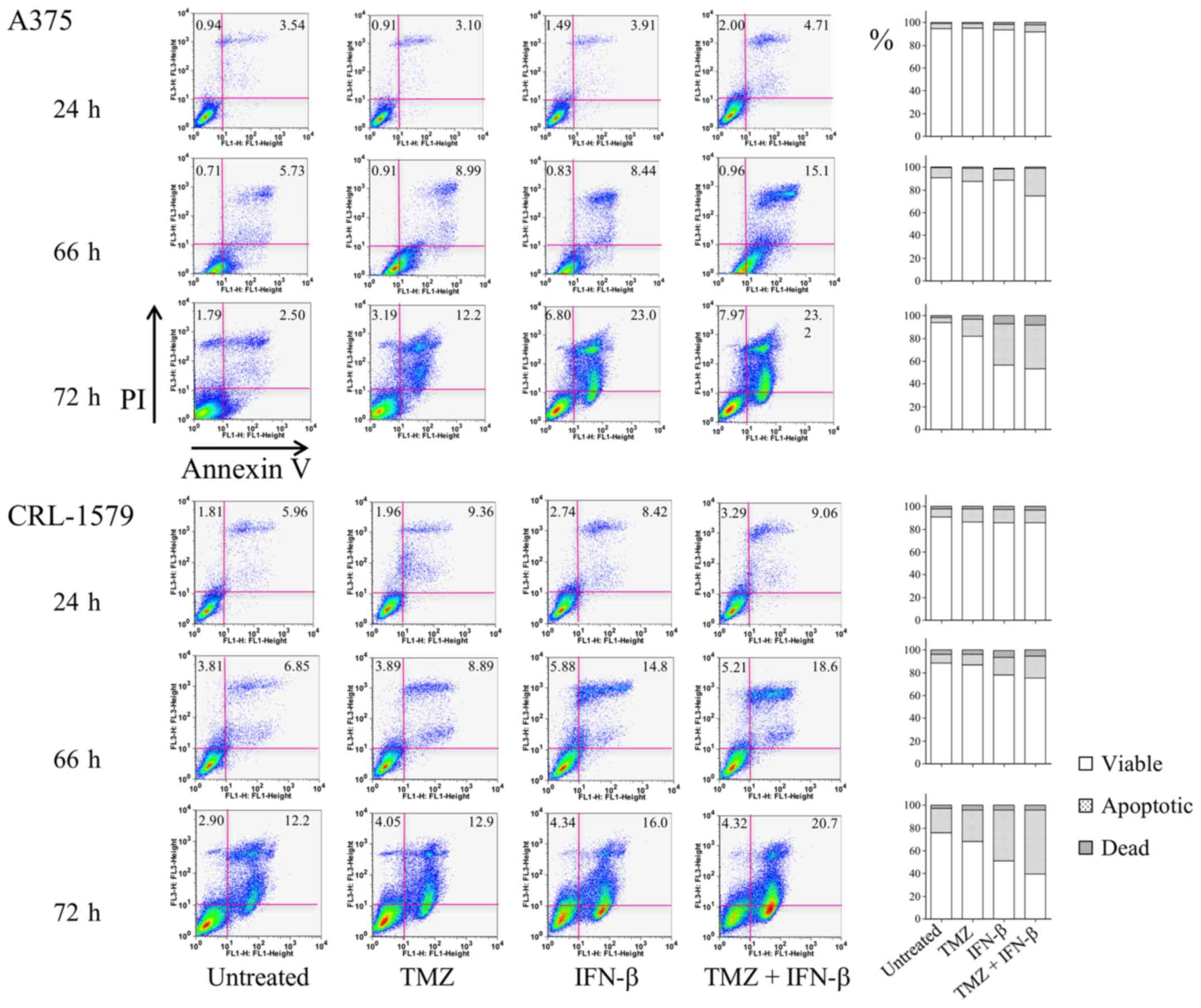
Interferon treatment for melanoma. While the precise mechanism of action remains poorly understood there are multiple antitumor effects of IFNα. Interferon belongs to cytokine family of proteins. Almost everyone who uses it experience mild to severe side effects.
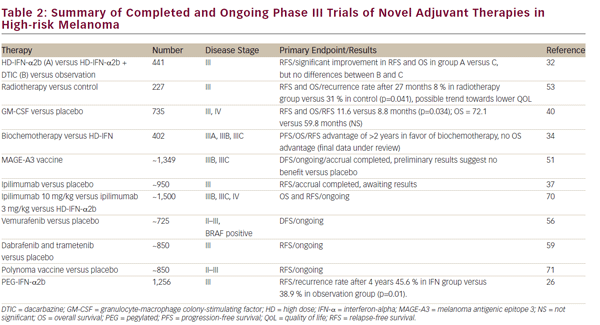
A quality-of-life-adjusted survival analysis of interferon alfa-2b adjuvant treatment for high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma. This together with questions over optimal treatment scheme and concerns over toxicity has limited its clinical use. This together with questions over optimal treatment scheme and concerns over toxicity has limited its clinical use.
State that the benefits of high-dose interferon are unrivalled by any other adjuvant treatment and that it is the standard of care for high-risk resected melanoma patients. Three types of man-made cytokines have been approved to treat melanoma skin cancer. While controversies are common in medicine few aspects of the treatment of malignant melanoma have stimulated as much controversy as the interpretation of the adjuvant interferon alfa IFNα trials for patients with resected high-risk melanoma.
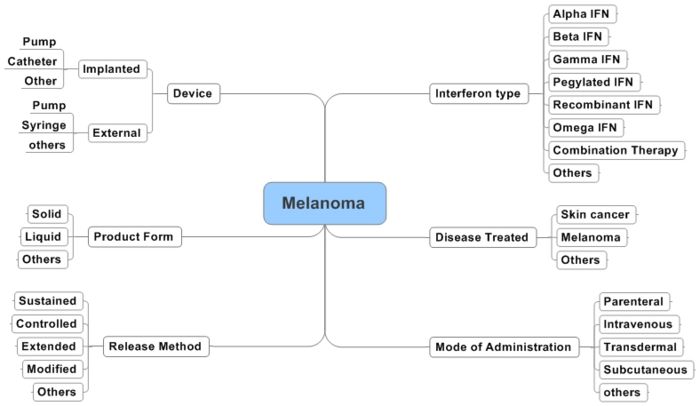
If youre having surgery to remove a melanoma your doctors might suggest interferon alfa Intron A Roferon -A afterward to help keep the melanoma from coming back. The degree to which interferon IFN alpha-2b offers real clinical benefits in the adjuvant therapy of melanoma at high risk of recurrence is a subject of debate. Of the multiple subsets of interferons IFNα has been shown to possess a reasonable degree of activity against melanoma.
The degree to which interferon IFN alpha-2b offers real clinical benefits in the adjuvant therapy of melanoma at high risk of recurrence is a subject of debate. Side effects can be harsh. To better assess the role of IFN-α an individual patient data IPD meta-analysis of these trials was undertaken.
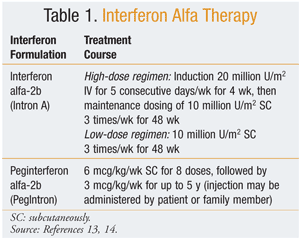
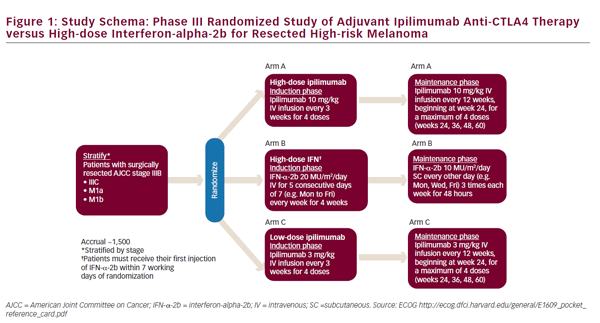
Following the removal of the primary melanoma interferon may stop the growth and spread of. Interferon therapy is initially administered directly into the blood stream intravenous during the first or induction phase. Neoadjuvant treatment of regional stage IIIB melanoma with high-dose interferon alfa-2b induces objective tumor regression in association with modulation of tumor infiltrating host cellular immune responses.
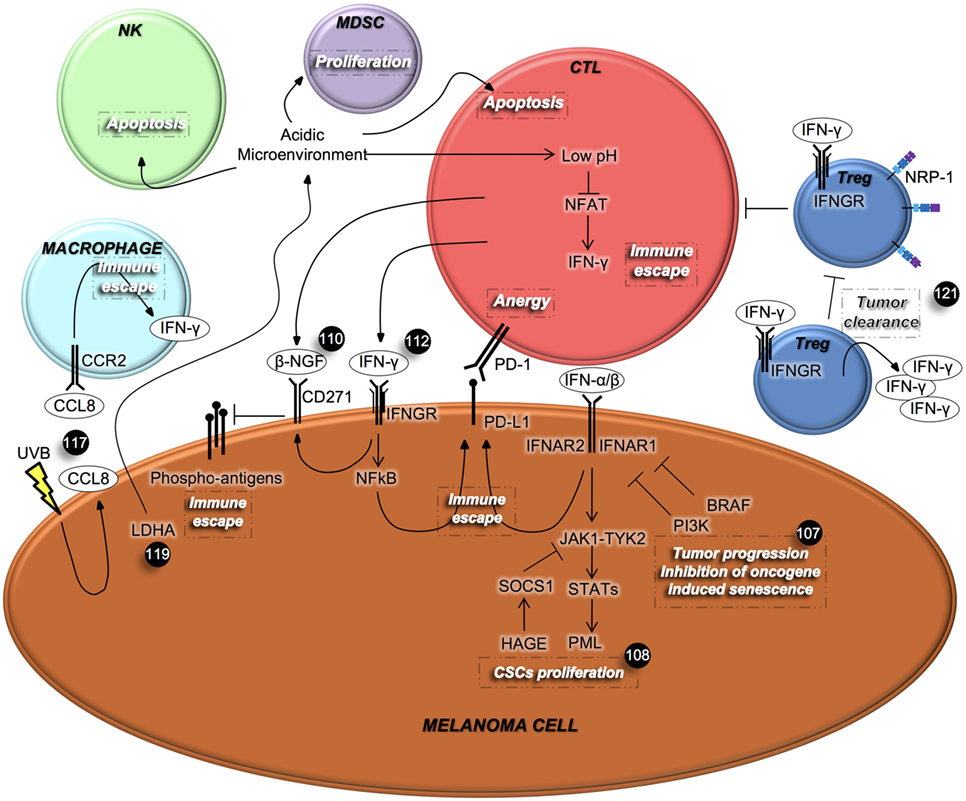
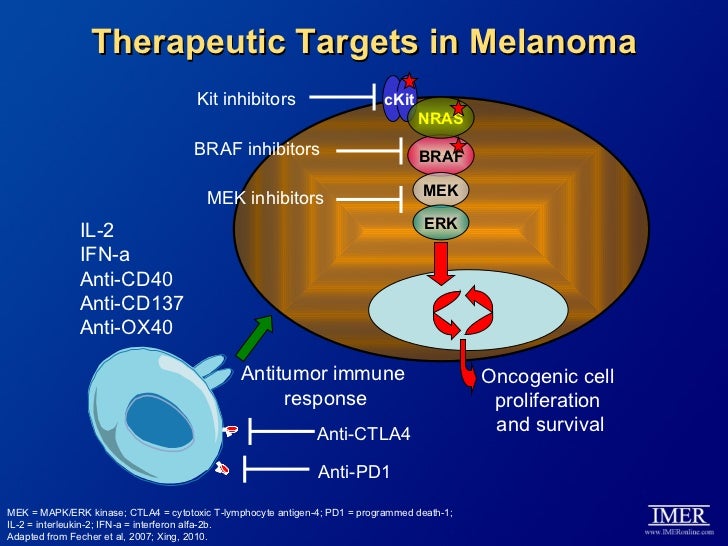
As adjuvant treatment for melanoma interferon-alpha is usually given in high doses for greater effectivity. The interferons are cytokines with diverse immunomodulatory effects on tumor cells.
However it can give many side effects.
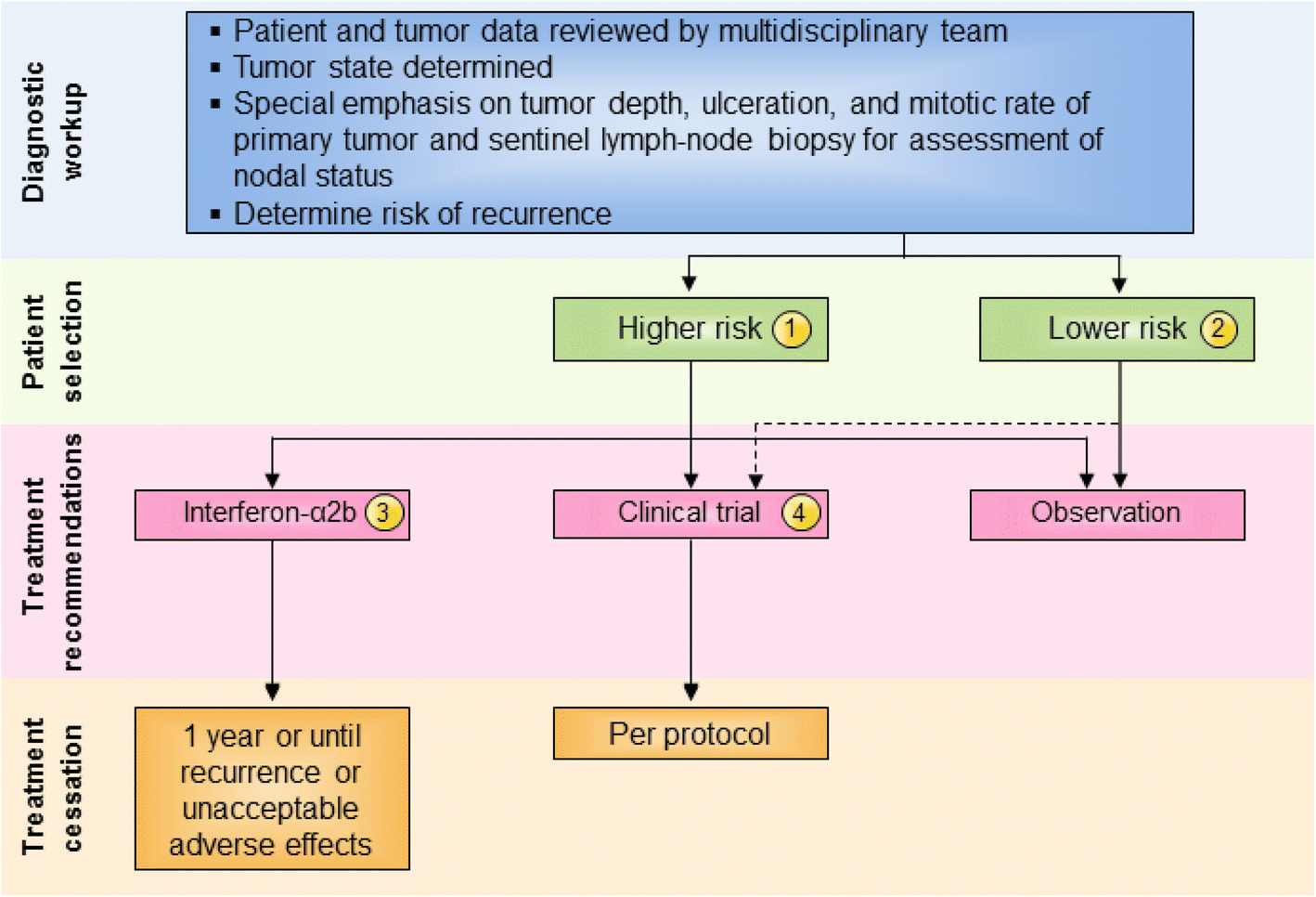
Following the removal of the primary melanoma interferon may stop the growth and spread of. Food and Drug Administration FDA approved to treat people who have had surgery to remove advanced melanoma tumors. In 1995 interferon became the first adjuvant therapy that the US. This together with questions over optimal treatment scheme and concerns over toxicity has limited its clinical use. To better assess the role of IFN-α an individual patient data IPD meta-analysis of these trials was undertaken. State that the benefits of high-dose interferon are unrivalled by any other adjuvant treatment and that it is the standard of care for high-risk resected melanoma patients. This involves injecting interferon five days per week for a 4-week period injection taking about 20-30 minutes. On the basis of a review of the literature an Italian Expert Panel. On the other hand Punt and Eggermont 2 conclude that the standard use of adjuvant high-dose interferon alfa cannot be recommended.
The use of high-dose IFN alfa for high-risk node-negative disease may occasionally be an alternative for patients with stage IIB or IIC disease but its use should be discouraged in favor of clinical trial participation or observation. On the basis of a review of the literature an Italian Expert Panel. State that the benefits of high-dose interferon are unrivalled by any other adjuvant treatment and that it is the standard of care for high-risk resected melanoma patients. Many randomised trials assessing interferon-α IFN-α as adjuvant therapy for high-risk malignant melanoma have been undertaken. Food and Drug Administration FDA approved to treat people who have had surgery to remove advanced melanoma tumors. This together with questions over optimal treatment scheme and concerns over toxicity has limited its clinical use. The use of high-dose IFN alfa for high-risk node-negative disease may occasionally be an alternative for patients with stage IIB or IIC disease but its use should be discouraged in favor of clinical trial participation or observation.


















/dermatologist-examines-a-mole-158875496-3ba6f127e7ba4d06a0f4da5426fdf39e.jpg)

















Post a Comment for "Interferon Treatment For Melanoma"